Daydream is the new interactive screensaver mode that was added in the Android 4.2 / Jelly Beans release. Such “dreams” may be activated when the device is in idle mode or inserted into a dock.
In the following tutorial we’re going to create a simple daydream that starts a simple animation and in addition we’ll be adding a configuration screen to alter the behaviour of this daydream.
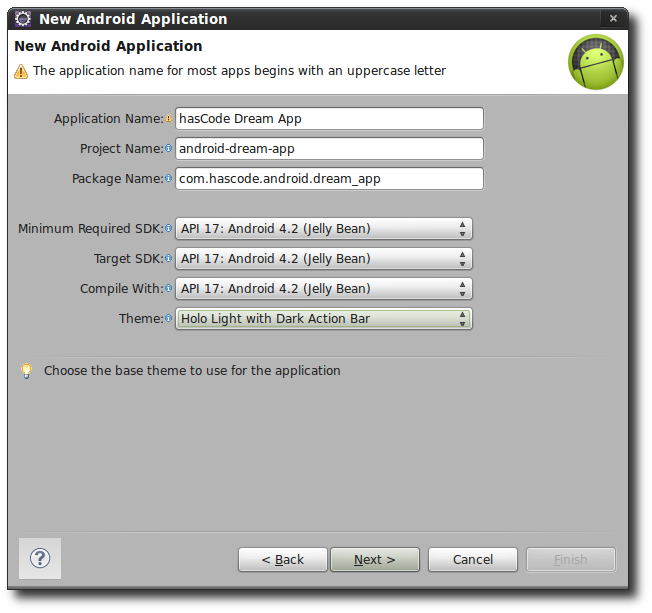
Create a new Android Application
First of all we need a new android project. I am using Eclipse and the ADT plugin here but any other solution like using a specific Maven archetype and the Jayway Maven plugin or using SBT should work, too.

Android Manifest
This is my basic AndroidManifest.xml – I am going to explain the specific sections that need to be added later – please just notice the manifest for now and keep on reading :)
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.hascode.android.dream_app"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="17"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
</application>
</manifest>Externalizing Strings
We’re externalizing all strings in a separate file – this is my res/values/strings.xml
<resources>
<string name="app_name">hasCode Dream App</string>
<string name="custom_dream_label">hasCode Dream</string>
<string name="demo_text">Dreaming of hasCode.com..</string>
<string name="toggle_animation">Animate Dream</string>
</resources>Creating the Dream Service
Now we’re nearly ready to create our dream service – the first step is to declare our service in the AndroidManifest.xml by adding the following service specification to the application element
<service
android:name="com.hascode.android.dream_app.SampleDream"
android:exported="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/custom_dream_label" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.service.dreams.DreamService" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</service>The Layout
In the next step we’re declaring a layout that should be displayed when our daydream is activated. Nothing special here for now – just a simple LinearLayout and a TextView – saved as res/layout/dream.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/animatedText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/demo_text"
android:typeface="monospace"
android:shadowColor="#000000"
android:shadowRadius="2."
android:shadowDx="4"
android:shadowDy="4"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" />
</LinearLayout>Adding an Animation
Displaying a simple text is not enough! We want at least some fancy, animated stuff here and that’s why we’re adding a custom animation that combines scaling, rotation and alpha changes and will be applied to the text view from the layout above.
If you’re interested in some further examples for animations on the Android platform, please feel free to take a look at my tutorial “https://www.hascode.com/2010/09/playing-around-with-the-android-animation-framework/[Playing around with the Android Animation Framework]“.
The animation is saved as res/anim/dream_animation.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<scale
android:duration="5000"
android:fillAfter="false"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:fromYScale="1.0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toXScale="3.0"
android:toYScale="3.0" />
<set>
<alpha
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="3000"
android:fromAlpha="0.2"
android:toAlpha="1.0" />
<rotate
android:duration="4000"
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:startOffset="700"
android:toDegrees="-360"
android:toYScale="0.0" />
<translate
android:duration="3000"
android:fromXDelta="100%"
android:fromYDelta="60%"
android:toXDelta="-20%"
android:toYDelta="-30%"
android:zAdjustment="bottom" />
</set>
</set>The Dream Service
Now last but not least our dream service – it serves the following purpose here:
-
load the daydream layout
-
lookup in the preferences if the user has enabled or disabled animations (I am covering this one chapter later)
-
if animations are not disable by user preference, load and start the animation
-
that’s all :)
The service should extend DreamService and offers some convenience methods to hook into the lifecycle or modify the display.
This is my implementation: SampleDream
package com.hascode.android.dream_app;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.service.dreams.DreamService;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SampleDream extends DreamService {
@Override
public void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
setInteractive(false);
setFullscreen(true);
setContentView(R.layout.dream);
TextView animatedText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.animatedText);
final SharedPreferences settings = getSharedPreferences(
CustomDreamSettingsActivity.PREFS_KEY, 0);
boolean animate = settings.getBoolean("animateDream", true);
if (animate) {
Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
R.anim.dream_animation);
animation.reset();
animatedText.startAnimation(animation);
}
}
}Adding a Configuration for the Dream Service
Now that we’ve got a theoretically running daydream we want to take a look how to add a configuration screen for our daydream. For this purpose a user shall be allowed to enable or disable the animation when the daydream is displayed.
So we need some sort of configuration view with some sort of a toggle button that allows the user to switch on/off the animation and this configuration view should be hooked into the place where the daydreams are managed in Android’s display settings.
First of all, we need to specify that there is meta data for our dream service. We do this by adding the following reference to the dream service’s service tag in the AndroidManifest.xml
<meta-data android:name="android.service.dream"
android:resource="@xml/hascode_dream" />Afterwards create the referenced file named hascode_dream.xml in the directory res/xml:
<dream xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:settingsActivity="com.hascode.android.dream_app/.CustomDreamSettingsActivity" />Now we have declared an activity CustomDreamSettingsActivity to handle our dream’s settings and we should in addition add the activity to the AndroidManifest.xml’s application element:
<activity android:name="CustomDreamSettingsActivity"></activity>Configuration Layout
We’re going the easy way here, we’re using a simple linear layout, a textview and a toggle button – that’s all…
The layout is saved as res/layout/dream_settings.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:gravity="center_horizontal" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/config_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/toggle_animation"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" />
<ToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle_animate_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checked="true"
android:minHeight="32dp"
android:minWidth="32dp" />
</LinearLayout>The Configuration Activity
Now we’re ready to create the activity to handle the dream’s settings. That means that the user input from the toggle button is saved using the shared preferences API.
That’s the way how we can disable and enable the animation from our dream service.
package com.hascode.android.dream_app;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener;
import android.widget.ToggleButton;
public class CustomDreamSettingsActivity extends Activity {
public static final String PREFS_KEY = "SampleDreamPrefs";
@Override
protected void onCreate(final Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.dream_settings);
final SharedPreferences settings = getSharedPreferences(PREFS_KEY, 0);
boolean animate = settings.getBoolean("animateDream", true);
final ToggleButton toggle = (ToggleButton) findViewById(R.id.toggle_animate_button);
toggle.setChecked(animate);
toggle.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(final CompoundButton buttonView,
final boolean isChecked) {
SharedPreferences.Editor prefEditor = settings.edit();
prefEditor.putBoolean("animateDream", isChecked);
prefEditor.commit();
}
});
}
}Running the Daydream
Now we’re ready to run and configure our daydream. Building the application and deploying it on a device should give us a similar look when tapping into our device → Settings > Display > Daydream.
As you can see there is a daydream listed with the ugly image/icon from my blog and a configuration button.
If you select the daydream and click on “Start now” you should see the sexiest animation ever some animation ;)

Pressing on the configuration-like-smelling button should start our configuration activity and enable us to disable or enable the animation when the daydream is started.

| I have put everything together for you in the following screencast on YouTube .. enjoy! ;) |
Tutorial Sources
Please feel free to download the complete project from my GitHub repository or check it out using Git:
git clone https://github.com/hascode/android-dream-tutorial.gitArticle Updates
-
2018-06-01: Embedded YouTube video removed (GDPR/DSGVO).